Meaning of Income Tax Return
Income Tax Return is a form or document that individuals and entities are required to file with the Income Tax Department, providing details of their income earned during a specific financial year. It includes information about various sources of income, deductions claimed, and tax payments made.
Who should file Income Tax Return in India?
As per the Income Tax Act, 1961, individuals and entities falling under the following categories are required to file ITR Return:
- Individuals: All individuals whose total income exceeds the basic exemption limit (currently INR 2.5 lakh for individuals below 60 years) are required to file ITR. This applies to salaried employees, self-employed professionals, freelancers, and others.
- Companies and firms: All registered companies and firms, irrespective of their profit or loss, are required to file ITR.
- Partnership firms and LLPs: Partnership firms and Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs) are required to file ITR.
- Trusts and Associations: Trusts, NGOs, charitable institutions, and other associations having income exceeding the exemption limit must file ITR Return.
Types of Income Tax Return Forms
The Income Tax Department has designed different types of ITR forms to cater to various categories of taxpayers. The appropriate form depends on the nature of income, sources of income, and the taxpayer’s residential status. Some commonly used ITR forms include:
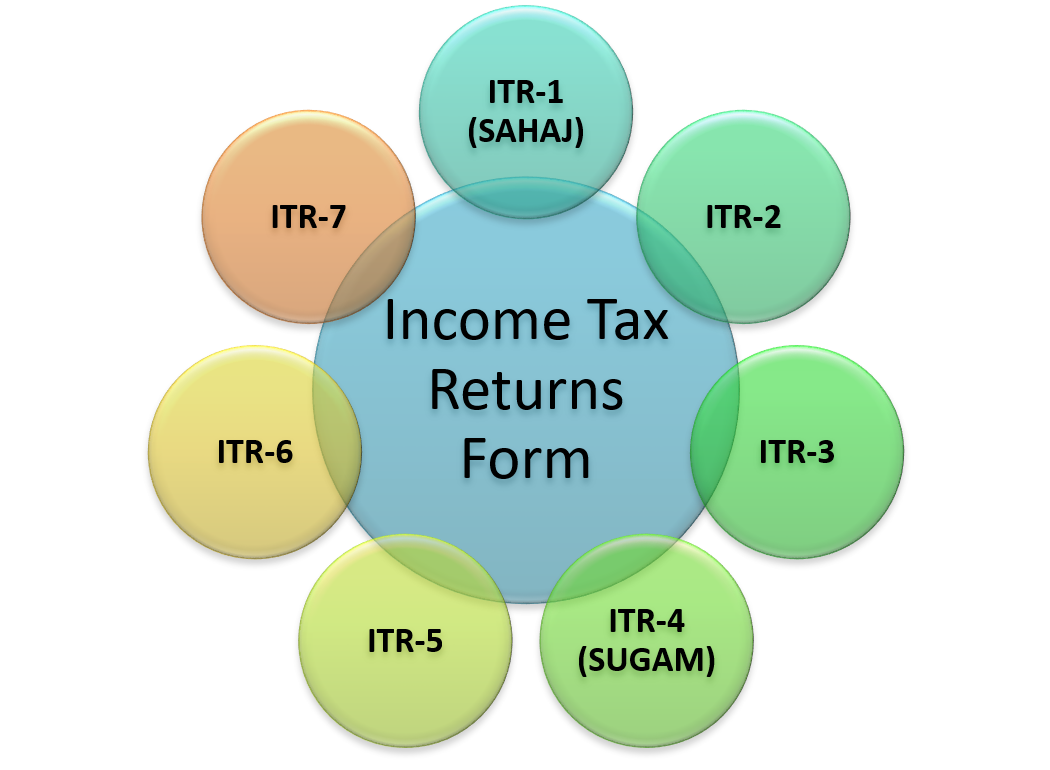
- ITR-1 (SAHAJ): This form is for individuals having income from salary, pension, one house property, or other sources (excluding lottery or racehorse income).
- ITR-2:This form is for individuals and Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs) not having income from business or profession.
- ITR-3: This form is for individuals and HUFs having income from a proprietary business or profession.
- ITR-4 (SUGAM): This form is for individuals, HUFs, and firms (other than LLPs) opting for presumptive taxation under Section 44AD, 44ADA, or 44AE of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
- ITR-5 : This form is for entities such as LLPs, Association of Persons (AOPs), and Body of Individuals (BOIs).
- ITR-6 : This form is for companies that are not claiming exemption under Section 11 of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
- ITR-7 : This form is for persons, including companies, who are required to furnish an ITR return under Sections 139(4A), 139(4B), 139(4C), or 139(4D) of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
Importance of ITR Filing in India
Income Tax Return Filing is an essential aspect of financial responsibility for individuals and businesses in India. It is a process through which taxpayers report their income, deductions, and tax liabilities to the government. While it may seem burdensome at times, filing income tax returns carries significant importance for both the taxpayers and the nation as a whole. The importance of ITR Filing in India are as follows:
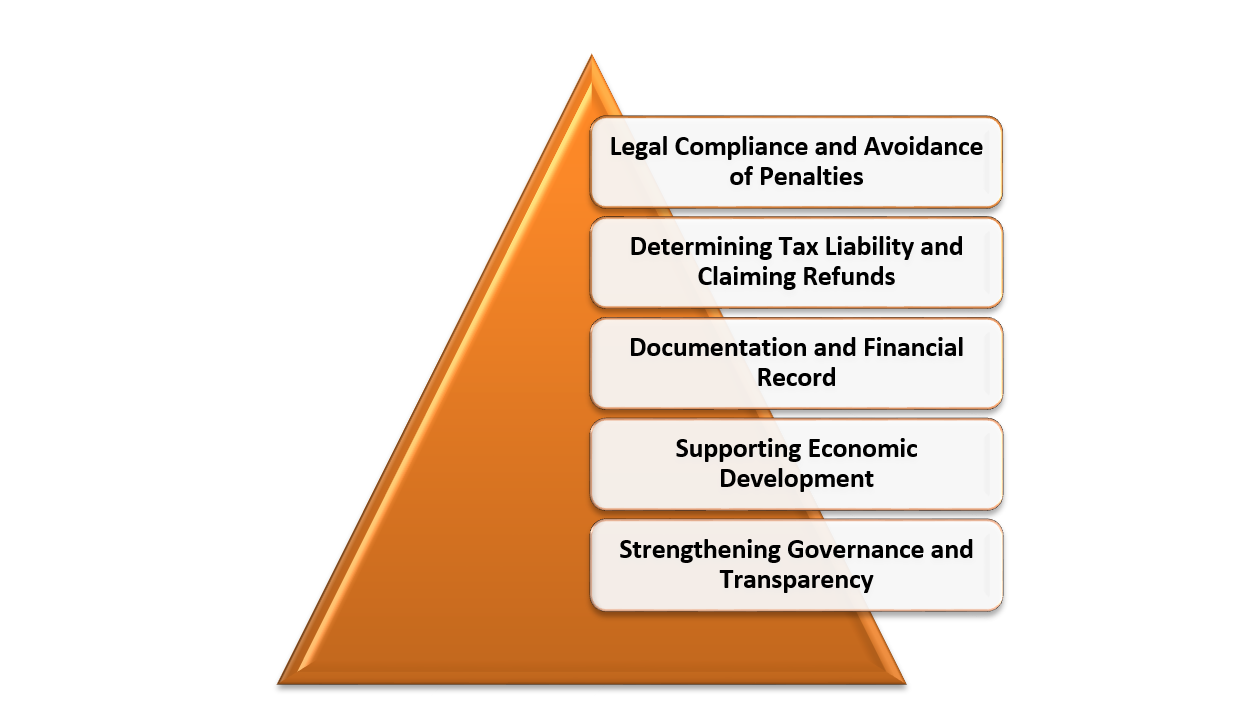
- Legal Compliance and Avoidance of Penalties: Filing income tax returns is a legal requirement mandated by the Income Tax Act, 1961 in India. It applies to individuals, Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs), partnership firms, companies, and any other entities that generate taxable income. By fulfilling this obligation, taxpayers demonstrate their compliance with the law and contribute to the nation’s economy.
Failure to file income tax returns can result in penalties, interest, and even legal consequences. The penalties can include fines and imprisonment, depending on the severity of the violation. Thus, filing tax returns on time helps taxpayers avoid unnecessary penalties and legal complications. - Determining Tax Liability and Claiming Refunds:The primary purpose of filing income tax returns is to determine the tax liability of individuals and entities. Through this process, taxpayers calculate their taxable income, apply relevant deductions and exemptions, and arrive at the final tax amount owed to the government. By correctly assessing their tax liability, taxpayers ensure they contribute their fair share to the development of the country.
Additionally, income tax return filing allows individuals to claim tax refunds. If a taxpayer has paid more taxes during the financial year than their actual liability, they can claim a refund by filing their returns. This refund can provide a much-needed financial boost and serve as an incentive for timely filing of tax returns. - Documentation and Financial Record: Income tax return filing helps in maintaining a comprehensive financial record. The process necessitates gathering and organizing relevant financial information, including income from various sources, expenses, investments, loans, and other financial activities. By documenting these details, taxpayers can keep track of their financial transactions, assess their financial health, and plan for the future.
Moreover, having an updated record of income tax returns is often required for various financial activities. For instance, when applying for loans, mortgages, or visas, individuals may need to provide their income tax returns as proof of income and financial stability. Hence, timely filing of returns ensures smooth financial operations and facilitates future endeavors. - Supporting Economic Development:Income tax plays a crucial role in funding the developmental projects and welfare programs undertaken by the government. It provides the necessary resources to build infrastructure, improve public services, and support initiatives aimed at socio-economic development. By filing tax returns honestly and accurately, taxpayers contribute to the nation’s progress and help create a better society for all citizens.
- Strengthening Governance and Transparency:Income tax return filing promotes good governance and transparency in the financial system. It helps the government in monitoring and regulating economic activities, reducing tax evasion, and identifying non-compliant individuals or entities. Through comprehensive reporting, tax authorities can track income patterns, detect discrepancies, and ensure fairness in the taxation system. This, in turn, leads to a more equitable distribution of resources and strengthens the overall governance framework.
Advantages of Income Tax Return Filing
The following are the advantages of ITR Filing in India:
Legal Compliance and Avoiding Penalties
One of the primary advantages of filing Income Tax Returns is to fulfill your legal obligations as a taxpayer. The Income Tax Act, 1961 mandates that individuals and businesses earning above the specified threshold file their tax returns. By complying with the law, you avoid penalties, fines, or legal complications that could arise from non-compliance.
Income Verification and Financial Transparency
Income Tax Return filing acts as a declaration of your income and assets to the government. It helps in establishing a clear record of your financial activities and offers transparency to tax authorities. This documentation becomes crucial in various situations, such as applying for loans, securing visas, or participating in government tenders, where your financial status may be scrutinized.
Claiming Tax Deductions and Refunds
Income Tax Returns provide an opportunity to claim various tax deductions and exemptions available under the Income Tax Act. These deductions can significantly reduce your tax liability and help you save money. Popular deductions include those for investments in tax-saving instruments (e.g., Employee Provident Fund, Public Provident Fund), health insurance premiums, home loan interest payments, and contributions to charitable organizations.
Additionally, filing income tax returns enables individuals to claim refunds if they have paid excess taxes during the financial year. Tax refunds can arise from sources like TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) or advance tax payments. By filing your returns, you can receive the refund due to you from the government, providing a welcome financial boost.
Establishing Financial History
Consistently filing income tax returns helps build a reliable financial history. This is particularly beneficial for individuals who plan to apply for loans or credit cards in the future. Lenders assess the creditworthiness of applicants based on their income tax return filings, making it essential to have a clean and consistent record. A positive financial history increases the likelihood of getting favorable loan terms, higher credit limits, and lower interest rates.
Avoiding Income Scrutiny
The Income Tax Department scrutinizes cases where individuals or businesses have not filed their tax returns or where discrepancies are detected. By filing your returns promptly and accurately, you minimize the chances of attracting the attention of the tax authorities for the wrong reasons. Proactive compliance reduces the risk of being subjected to income tax audits, notices, or investigations.
Financial Planning and Budgeting
Filing income tax returns requires individuals to compile and organize their financial information. This process encourages better financial planning and budgeting. By evaluating your income, expenses, investments, and savings, you gain a comprehensive understanding of your financial standing. It allows you to identify areas for improvement, make informed decisions, and optimize your financial resources effectively.
Contributing to Nation Building
Filing income tax returns is a fundamental way to contribute to the development and progress of the nation. Income tax revenue forms a significant part of the government’s income, which is utilized for infrastructure development, social welfare programs, education, healthcare, defense, and more. By fulfilling your tax obligations, you actively participate in the nation-building process and help create a better society for all.
Documents required for Income Tax Return Filing in India
To complete the income tax return filing process accurately and efficiently, it is essential to gather and organize the necessary documents. The following are the documents required for ITR Filing:
- PAN Card: Permanent Account Number ( PAN ) is a unique identification number issued by the Income Tax Department. It is a mandatory document for filing income tax returns.
- Aadhaar Card: Aadhaar is a 12-digit unique identification number issued by the Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI). Linking your Aadhaar card with your PAN card is compulsory for income tax return filing.
- Form 16: Form 16 is issued by your employer and provides details of your salary, allowances, deductions, and Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) during the financial year. It is an essential document for salaried individuals.
- Form 16A: Form 16A is similar to Form 16 but is issued by entities other than employers, such as banks, for TDS on income other than salary. It is relevant for individuals receiving income from fixed deposits, interest on securities, etc.
- Form 26AS: Form 26AS is a consolidated statement that shows the tax credits available to you based on TDS deducted by your employer, banks, or other deductors. It is crucial for cross-verification and reconciliation while filing your tax returns.
- Bank Statements: Maintain a record of your bank statements for the financial year. It helps in verifying the income earned, interest received, and expenses claimed during the year.
- Investment Proofs: Gather proofs of your investments made during the financial year to claim deductions under various sections of the Income Tax Act, 1961. This includes documents related to investments in Public Provident Fund (PPF), National Savings Certificates (NSC), tax-saving fixed deposits, life insurance premiums, and other eligible investment instruments.
- Property Documents: If you own property, ensure you have the necessary documents like sale deed, purchase agreement, and home loan statements. These documents are required to claim deductions on home loan interest and principal repayments.
- Rent Receipts: If you are a salaried individual living in a rented house and want to claim House Rent Allowance (HRA) exemption, keep rent receipts handy. Make sure they are appropriately stamped and contain the necessary details such as landlord’s name, address, and PAN (if applicable).
- Other Documents: Keep any other supporting documents that may be relevant to your income tax return filing, such as charitable donations receipts, medical bills for claiming medical reimbursements, and proofs of deductions under Section 80D (health insurance premiums).
Steps for Income Tax Return Filing
-
Step 1: Determine the Applicable Income Tax Return Form
The first step in filing your income tax return is to determine the appropriate form to use. The Income Tax Department of India provides several forms for different types of taxpayers, such as individuals, Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs), companies, and partnerships. The commonly used forms for individuals are ITR-1 (Sahaj), ITR-2, ITR-3, and ITR-4. Carefully assess your sources of income and choose the form that suits your situation.
-
Step 2: Gather the Required Documents
Before starting the income tax return filing process, gather all the necessary documents. These may include your PAN (Permanent Account Number) card, Aadhaar card, bank statements, Form 16 (provided by your employer), Form 16A (for income from other sources), details of investments, and any other relevant financial documents. Having these documents readily available will help you provide accurate information while filing your return.
-
Step 3: Compute Your Income and Tax Liability
The next step is to compute your total income for the financial year. Consider all sources of income, such as salary, house property, capital gains, business or profession, and other incomes. Deduct eligible expenses, deductions, exemptions, and allowances to arrive at your taxable income. Use the income tax slabs and rates applicable for the financial year to calculate your tax liability accurately.
-
Step 4: File Your Income Tax Return Online
The Income Tax Department has made it mandatory for most taxpayers to file their income tax returns online. Visit the official website of the Income Tax Department (https://www.incometaxindiaefiling.gov.in) and register yourself as a taxpayer. Once registered, log in to your account and select the relevant income tax return form. Fill in the necessary details, such as personal information, income details, and deductions. Double-check the information provided before submitting the return.
-
Step 5: Verify and Submit Your Return
After filling in the required details, verify your income tax return. The Income Tax Department provides multiple verification methods, such as using Aadhaar OTP (One-Time Password), generating and sending a signed physical copy of ITR-V to the Centralized Processing Centre (CPC), or using Electronic Verification Code (EVC). Choose the verification method that suits you and complete the verification process.
-
Step 6: Keep Proof of Filing
After successfully filing your income tax return, ensure that you keep a copy of the filed return for future reference. It is advisable to retain copies of Form 16, Form 16A, and any other relevant documents supporting the information provided in your return. These documents may be required for audit purposes or while applying for loans or visas.
-
Step 7: Pay Any Remaining Tax Liability
If, after filing your return, you find that you have a tax liability, make the payment as per the guidelines provided by the Income Tax Department. Utilize the authorized modes of payment, such as net banking or debit/credit card, to pay the outstanding tax amount. Remember to pay any due taxes before the specified due dates to avoid penalties and interest charges.
-
Step 8: Respond to Notice, if Received
In some cases, the Income Tax Department may send a notice seeking additional information or clarification regarding your income tax return. If you receive such a notice, respond promptly and provide the requested details. Ignoring or delaying the response may lead to further complications, including penalties.
Income Tax Filing deadlines for the Financial Years 2023-24 (Academic Years 2024-25)
The Income tax filing due dates for FY 2023-24 (AY 2024-25) are as follows:
Sr. No. | Category of the Tax Payer | Income Tax Filing deadlines for the FY 2023-24 (AY 2024-25) |
1. | Individual / HUF / AOP / BOI (no need for audited books of accounts) | 31st July 2024 |
2. | Businesses (With Audit) | 31st October 2024 |
3. | Businesses that require transfer pricing reports (for international/specified domestic transactions) | 30th November 2024 |
4. | Return Revised | 31 December 2024 |
5. | Late Return | 31 December 2024 |
Penalty in case of late ITR Filing as per Income Tax Act, 1961
The following are the penalty may be imposed on taxpayer in case of late income tax return filing:
Section 234F: Late Filing Fees
Section 234F was introduced in the Income Tax Act, 1961, in order to encourage timely filing of income tax returns. According to this section, if an individual or Hindu Undivided Family (HUF) fails to furnish the income tax return within the specified due date, they are liable to pay a late filing fee. The applicable fees under Section 234F are as follows:
- If the return is filed after the due date but on or before December 31 of the assessment year (AY), a late filing fee of Rs. 5,000 is applicable.
- If the return is filed after December 31 of the AY, a late filing fee of Rs. 10,000 is applicable.
However, there is a relief provision for small taxpayers. If the total income of the individual does not exceed Rs. 5, 00,000, the maximum fee payable is restricted to Rs. 1,000.
It is important to note that the late filing fee under Section 234F is not applicable to individuals who are 80 years or older at any time during the relevant financial year.
Interest on Delayed Payment
Apart from the late filing fees, the Income Tax Act, 1961, also imposes interest on delayed payment of taxes. If the taxpayer fails to pay the income tax liability within the due date, they will be liable to pay interest under Section 234A, 234B, and 234C of the Act. Let’s understand these sections in detail:
Section 234A: Interest for Delay in Filing Return
Under Section 234A, if a taxpayer fails to file the income tax return within the due date, they are liable to pay interest at the rate of 1% per month or part thereof. This interest is calculated from the due date of filing the return until the actual date of filing.
Section 234B: Interest for Default in Payment of Advance Tax
If a taxpayer fails to pay the advance tax or pays an amount less than the required installment, they will be liable to pay interest under Section 234B. The interest rate is 1% per month or part thereof, calculated from the due date of advance tax installment until the actual payment of tax.
Section 234C: Interest for Default in Payment of Quarterly Installments
Section 234C applies to individuals who are liable to pay advance tax in installments. If the taxpayer fails to pay the required installment or pays an amount less than the prescribed percentage, they will be liable to pay interest under Section 234C. The interest is calculated at the rate of 1% per month or part thereof for the period of default.
Prosecution and Other Consequences
Apart from the penalties mentioned above, the Income Tax Act, 1961, also includes provisions for prosecution and other consequences in case of willful non-compliance or fraud. If a taxpayer willfully fails to furnish the income tax return or provides false information, they may face legal action, which could include prosecution, imprisonment, or both, along with the imposition of penalties.
It is important for taxpayers to understand their obligations under the Income Tax Act, 1961, and adhere to the specified timelines for filing income tax returns. Timely compliance not only helps avoid penalties but also ensures a smooth tax filing process and maintains the integrity of the taxation system.
Way Forward
In conclusion, ITR filing is a crucial responsibility for individuals and entities in India. By understanding the process, gathering the necessary documents, computing income and tax liability accurately, and adhering to the deadlines, taxpayers can fulfill their obligations effectively. It is advisable to stay updated with the latest rules and guidelines issued by the Income Tax Department to ensure compliance and avoid any penalties or legal issues.
