Introduction
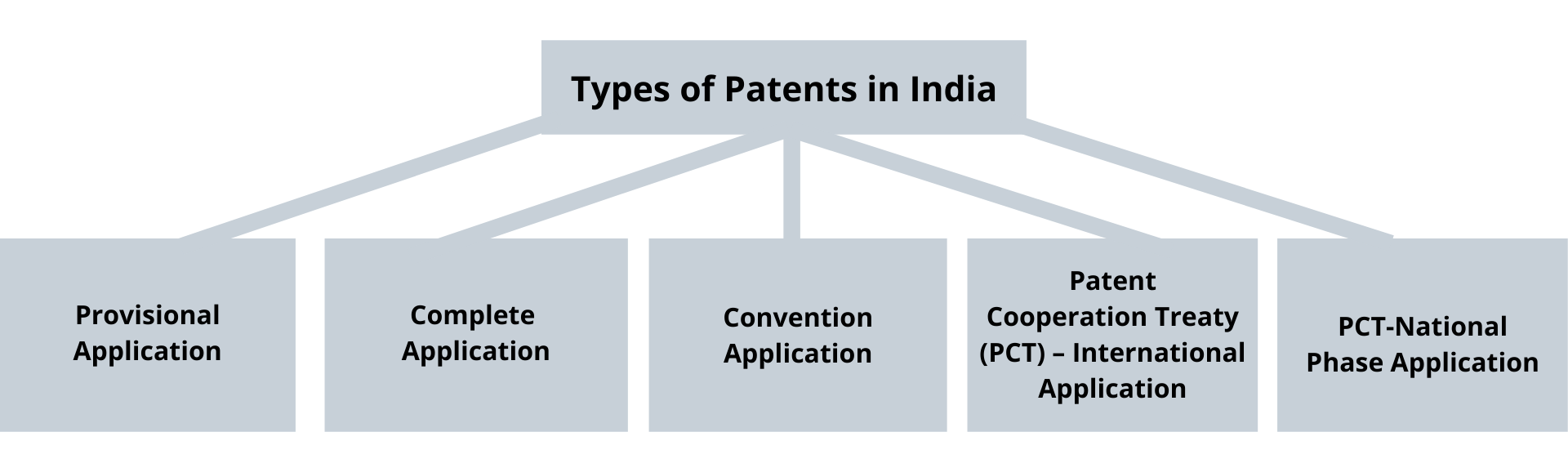
India has perpetually been a land of inventions whether you talk about jaipur foot, plastic surgery, optic fibre or zero. To supplement these inventions a patent act, 1970 was brought into light, which was enforced on 20th April, 1972. Inventing something takes on variant efforts and time therefore is the process of registration of patent. To scale back this cumbersome patent application, drafting office is established to supervise the sitting provisions and laws. Basically there are five types of patents in India
How to Register Patent In India ?
- Pen down the invention in detail
The various aspects of invention must be pen down like the subject matter, its mechanism, perks to society, etc. For proof work records or other documents should be presented duly signed and dated by the respective authority. For better visual illustrations drawings or diagrams of working or product should conjointly designed.
- Check invention patentable status
Under Indian patent act, all inventions could not be registered under section 3 and 4 of the patent act, 1970 . The following inventions are not patentable:
- Anything contrary to well established natural laws.
- Whose primary or business exploitation of that can be contrary to public order or morality or which causes serious prejudices to human, animal or flora or health or to the environment.
- Mere discovery of a scientific principle or formulation of an abstract theory or discovery of any living o non living thing substances occurring in nature.
- Mere discovery of a brand new form of a known substance that does not ends up in the enhancement of the known effectiveness of that substance or the mere discovery of any new property or new use for a known substance or of the mere use of a known process, machine or apparatus unless such known process results in a new product or employs at least one new reactant.
- A substance obtained by a mere admixture ensuing solely within the aggregation of the properties of the components thereof or a process for producing such substance.
- Mere arrangement or rearrangement or duplication of known devices each functioning severally of one another in a known way.
- Method of agriculture or horticulture.
- Any method of the medicative, surgical, curative, prophylactic, diagnostic, therapeutic or alternative treatment of human beings or any process similar for treating animals to render them free of diseases or to increase their economic value or that of their products.
- Plants and animals in whole or any part thereof other than micro organisms but including seeds, varieties and species and essentially biological processes for production or propagation of plants and animals.
- Mathematical or business method or a computer programme or algorithms
- Literary, dramatic, musical or artistic work or any other aesthetic creation whatsoever including cinematographic works and television productions.
- Mere scheme or rule or method of performing mental act or method of playing game.
- Presentation of information.
- Topography of integrated circuits.
- Invention which in effect, is traditional knowledge or which is an aggregation or duplication of known properties of traditionally known component or components.
- And according to section 4, inventions relating to atomic energy.
- Meeting patentability criteria
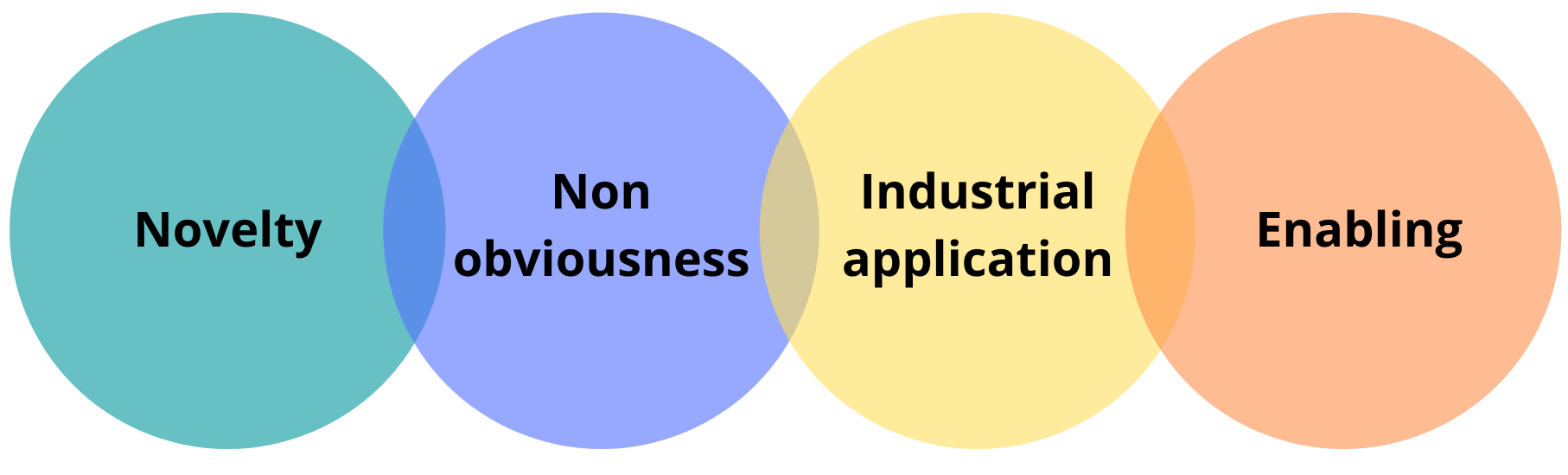
The Indian patent act establishes certain criteria for an invention being patented i.e.
After examining all the aspects it must be decided whether to go ahead with the invention or not. This will result in saving a lot of time, efforts and cost.
- Filing patent application
If you are at an early stage of your research then it advisable to file a provisional application as it saves money, secures dates with a 12 months’ time period to file complete specification. This is an optional step for convenience.
At the expiry of the same the application will automatically vanish if the complete specification is not filed. When the research and documents are completed and invention is ready for prototype then complete specification patent application can be filed. If you are already done with your invention then you can directly file the latter application.
- Publication
After filing the complete specification in conjunction with application for patent, the same is published after 18 months of first filing. Exceptionally, a request for early publication could also be made along with the prescribed fees if don’t want to wait till the above limit.
- Examination request
Patent application can be examined by a request for examination (RFE). On receiving the previous the controller hands over the application to patent examiner for scrutiny. The examiner examines the patent application on the premises on certain principles like
- Patentable subject matter
- Novelty
- Non obviousness
- Inventive step
- Industrial application
- Enabling
After evaluating the application the report is made i.e., patent prosecution (everything happening to patent application before grant of approval is called patent prosecution) which is handed over to applicant ultimately.
- Reply to objections
Nine of ten applicants will receive objection based on examination report. In this case it is advisable to seek a professional to draw an analysis on report and form response clearly communicating the controller about the novelty and patentability of invention.
- Clarifying objections
This to and fro of thoughts will help in eradicating the mist over the prior arts (existing documents before date of filing) to the controller. On satisfaction of the authority the application will be forwarded for approval as soon as possible otherwise the same will be discarded.
- Grant of patent
Once the application meets all the grounds for patentability, the same will be approved. On the approval the grant of patent will be notified in the patent journal which is published time to time.



