
Introduction
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) play a significant role in contributing to India’s economy. However, with the implementation of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India, NRIs may find themselves wondering whether they need GST registration. This article aims to shed light on the subject and provide clarity on the question, “Do NRIs need GST registration in India? “Whether you are an NRI conducting business in India or an individual seeking clarity on GST obligations, this article will equip you with the knowledge necessary to navigate the complexities of GST registration for NRIs. Let’s explore the requirements and implications of GST registration process for NRIs in India and gain a comprehensive understanding of this important aspect of doing business in the country.
| Table of Content |
GST Registration in India
GST (Goods and Services Tax) registration in India is a mandatory requirement for businesses that meet certain criteria. GST is a comprehensive indirect tax levied on the supply of goods and services across the country. To register for GST, a business must have a turnover above the specified threshold, which varies based on the state and nature of the business. The registration process involves obtaining a unique Goods and Services Tax Identification Number (GSTIN) from the government.
To register, businesses need to provide various documents, such as PAN (Permanent Account Number) card, proof of business ownership, address proof, bank account details, and authorized signatory details. Once the application is submitted online through the GST portal, it is verified by the tax authorities. Upon successful verification, the GSTIN is issued, allowing the business to collect and remit GST on its supplies. GST registration brings several benefits, including the ability to avail input tax credit, easier compliance, and enhanced credibility for the business.
Determining the applicability of GST for NRIs
It is important for NRIs to understand their residential status, the nature of their activities, and the GST provisions in India to determine the applicability and compliance requirements for their transactions.
- Residential Status: The applicability of GST for Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) depends on their residential status. NRIs who are considered residents under the Income Tax Act are subject to GST on their activities in India.
- Place of Supply: GST is applicable to NRIs if they supply goods or services from outside India to individuals or businesses located in India. The place of supply rules determines whether GST is applicable, based on the location of the supplier and the recipient of the goods or services.
- Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM): If an NRI receives goods or services in India on which the supplier is not registered under GST, the recipient (NRI) is liable to pay GST under the reverse charge mechanism. This means the NRI is responsible for paying the applicable GST directly to the tax authorities.
- Import of Goods: NRIs importing goods into India are subject to GST. The GST is levied at the time of importation, and the NRI is responsible for paying the applicable GST, customs duties, and other charges.
- Exports and Export-related Services: GST is not applicable to the export of goods or services by NRIs. Exports are considered zero-rated under GST, meaning no GST is levied on the supply. However, certain conditions and documentation need to be met to claim zero-rated benefits.
Circumstances Requiring GST Registration for NRIs
A. Supply of taxable goods and services in India
NRIs who supply taxable goods or services within India are generally required to register for GST. The term “supply” refers to any transaction involving the transfer of goods or services for consideration, including sales, transfers, exchanges, leases, and more. If an NRI is engaged in such activities in India, they need to register for GST to comply with the tax laws.
B. Operating a business in India
NRIs operating a business in India, either as a sole proprietorship, partnership, or company, are generally obligated to register for GST. It applies to both online and offline businesses. If an NRI’s business involves the supply of taxable goods or services, regardless of the scale or turnover, GST registration becomes mandatory to ensure compliance with the tax regulations.
C. Threshold limits for GST registration
GST registration becomes mandatory for NRIs if their annual aggregate turnover exceeds the prescribed threshold limits. For regular businesses, the threshold limit is generally INR 40 lakhs (INR 20 lakhs for special category states). However, specific categories of businesses may have lower or higher threshold limits, such as INR 10 lakhs for businesses in northeastern states and hilly regions.
GST Registration process for NRIs
The process of GST registration for NRIs (Non-Resident Indians) in India involves the following steps:
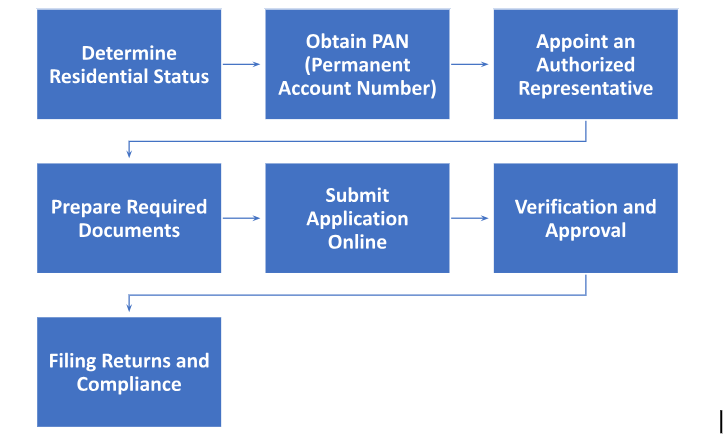
- Determine Residential Status: NRIs should first ascertain their residential status under the Income Tax Act to understand if they are eligible for GST registration.
- Obtain PAN (Permanent Account Number): NRIs must have a valid PAN issued by the Indian Income Tax Department. If they do not have a PAN, they can apply for it online through the NSDL or UTIITSL websites.
- Appoint an Authorized Representative: NRIs under GST need to appoint an authorized representative in India who will act on their behalf for GST-related matters. The authorized representative can be an individual or an entity with a valid PAN.
- Prepare Required Documents: Gather the necessary documents for GST registration, which typically include:
- Passport: A copy of the passport showing the name, photograph, and signature of the NRI.
- Proof of Address: Documents such as a bank statement, utility bill, or rental agreement that establish the NRI’s overseas address.
- Bank Account Details: Provide the bank account details, including the bank statement or canceled cheque.
- Authorized Representative Documents: If an authorized representative is appointed, their identity proof and address proof should be submitted.
- Submit Application Online: Access the GST portal (https://www.gst.gov.in/) and complete the registration application online. Provide the necessary details, including PAN, authorized representative details, and upload the required documents.
- Verification and Approval: The application will be scrutinized by the GST authorities, who may request additional documents or clarification if needed. Once the application is reviewed and deemed complete, the GST registration will be approved, and a unique Goods and Services Tax Identification Number (GSTIN) will be issued.
- Filing Returns and Compliance: After obtaining the GSTIN, NRIs must fulfill their GST compliance obligations, including filing periodic GST returns, maintaining proper records, and paying GST dues if applicable.
Responsibilities and Compliance for NRI GST Registrants
NRIs (Non-Resident Indians) who have registered for Goods and Services Tax in India have specific responsibilities and compliance requirements to adhere to. Here are the key aspects:
- Collecting and Remitting GST: NRIs engaged in taxable supplies of goods or services in India are required to collect GST from their customers. The applicable GST rates and proper invoicing procedures must be followed. The collected GST should be remitted to the government within the prescribed timelines.
- Filing GST Returns: NRIs with GST registration need to file regular GST returns. The frequency of return filing depends on the turnover and nature of the business. The returns include details of outward supplies (GSTR-1), inward supplies (GSTR-2), and a summary return (GSTR-3). Late filing or non-filing of returns may attract penalties and interest.
- Compliance with Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM): If an NRI receives goods or services from unregistered suppliers in India, they are responsible for paying GST under the reverse charge mechanism. The NRI must calculate and remit the applicable GST to the government using the appropriate GST return.
- Maintenance of Records: NRIs must maintain proper records of their business transactions, including invoices, bills of supply, import/export documents, and GST payment receipts. These records should be maintained for at least six years from the end of the financial year they pertain to.
- Compliance with Input Tax Credit (ITC) Provisions: NRIs can claim input tax credit for GST paid on inputs, input services, and capital goods used in their business. However, they need to comply with the prescribed conditions and maintain the necessary documents to support the claim for ITC.
- Addressing GST Notices and Communications: NRIs should regularly monitor their GST portal account and address any notices, communications, or inquiries from the GST authorities promptly. Failure to respond within the specified time can lead to penalties and further compliance issues.
- Timely Payment of GST Dues: NRIs must ensure timely payment of GST dues to the government within the prescribed due dates. Late payment may attract interest and penalties.
Conclusion
In conclusion, GST registration for NRIs in India is subject to certain criteria and compliance obligations. NRIs must determine their residential status, obtain a PAN, appoint an authorized representative, and submit the necessary documents online through the GST portal. Once registered, NRIs have specific responsibilities, including collecting and remitting GST, filing regular GST returns, complying with the reverse charge mechanism, maintaining records, claiming input tax credit, addressing notices and communications, and ensuring timely payment of GST dues. Compliance with these requirements is essential to avoid penalties and maintain a smooth business operation. Understanding and adhering to the regulations contribute to a transparent and efficient GST system for NRIs conducting business activities in India.


