
AOC-4, a crucial financial statement filing under the Companies Act, 2013, is indeed applicable to Section 8 companies. These unique entities, primarily formed for charitable or non-profit purposes, are not exempt from Section 8 company compliance requirements. AOC-4 mandates Section 8 companies to submit their financial statements, including the balance sheet, profit and loss account, and cash flow statement, to maintain transparency and accountability. This ensures that even organizations driven by social objectives adhere to statutory financial reporting standards, promoting trust and credibility among stakeholders. In this article, we will delve deeper into the significance of AOC-4 compliance for Section 8 companies and the steps involved in fulfilling this legal obligation.
| Table of Content |
Define AOC-4
AOC-4, in the context of Indian corporate governance, is a crucial financial statement filing mandated by the Companies Act, 2013. This document serves as an annual financial report submitted by registered companies to the Ministry of Corporate Affairs. AOC-4 primarily includes financial statements such as the balance sheet, profit and loss account, and cash flow statement. These statements offer a comprehensive view of a company’s financial health, performance, and compliance with accounting standards. AOC-4 is a vital tool for transparency, accountability, and regulatory compliance, ensuring that companies adhere to established financial reporting norms and fostering trust among stakeholders, investors, and the government.
Section 8 companies and their purpose
Section 8 companies, also known as not-for-profit companies under the Companies Act, 2013 in India, are unique legal entities with a specific purpose and structure. Their primary purpose is to promote charitable or non-profit objectives while ensuring compliance for Section 8 companies. Here’s an overview of Section 8 companies and their purposes:
- Charitable and Social Causes: The main aim of Section 8 companies is to promote activities related to social welfare, education, art, culture, science, religion, charity, protection of the environment, or any other similar object that benefits society as a whole.
- No Profit Distribution: Section 8 companies are prohibited from distributing any profits or dividends among their members.
- Limited Liability: Members of Section 8 companies have limited liability, meaning they are not personally responsible for the company’s debts or liabilities.
- Legal Framework: Section 8 companies must adhere to the legal framework outlined in the Companies Act, 2013, and they are subject to regulatory oversight by the Registrar of Companies (RoC).
- Tax Benefits: These companies can also avail tax benefits and exemptions under certain conditions, which makes them attractive for donors and contributors looking to support charitable causes.
Applicability of AOC-4 to Section 8 companies
The applicability of AOC-4 to Section 8 companies is a critical aspect of their annual compliance, ensuring they meet the necessary regulatory requirements. Section 8 company annual compliance, including the filing of AOC-4, is essential for maintaining transparency and accountability in their operations. These not-for-profit entities must submit this financial statement to the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, showcasing their adherence to accounting standards and financial reporting norms. This annual compliance for Section 8 companies demonstrates their commitment to their charitable or non-profit objectives while upholding legal obligations and the trust of stakeholders.
Steps for AOC-4 Compliance by Section 8 Companies
Ensuring AOC-4 compliance for Section 8 companies involves several steps, covering ROC compliance for Section 8 companies, income tax compliance, and compliance under the Companies Act, 2013. Here’s a breakdown:
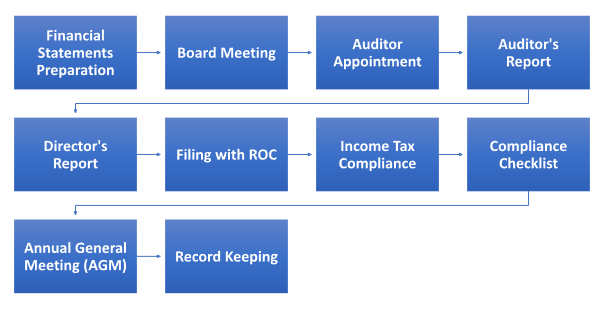
- Financial Statements Preparation: Section 8 companies must start by preparing their financial statements, including the balance sheet, profit and loss account, and cash flow statement, by the prescribed accounting standards.
- Board Meeting: Convene a board meeting to approve the financial statements and the director’s report, ensuring alignment with Section 8 company compliance requirements.
- Auditor Appointment: Appoint a statutory auditor or auditors to review and audit the financial statements. Compliance with Section 8 under the Companies Act, 2013, mandates that auditors must be chartered accountants.
- Auditor’s Report: Obtain the auditor’s report, which should include their opinion on the financial statements’ accuracy and compliance with accounting standards.
- Director’s Report: Prepare the director’s report, highlighting the company’s activities, financial performance, and social impact, in line with Section 8 company annual compliance.
- Filing with ROC: Complete the AOC-4 form, which includes the financial statements and auditor’s report. Submit this electronically to the Registrar of Companies (ROC) within the prescribed timeframe.
- Income Tax Compliance: Ensure income tax compliance by filing the necessary income tax returns, if applicable, and availing any tax exemptions or benefits Section 8 companies may be eligible for.
- Compliance Checklist: Regularly review and update a compliance checklist to track Section 8 company annual compliance requirements under the Companies Act, 2013.
- Annual General Meeting (AGM): Convene the AGM within the stipulated time frame and present the financial statements and auditor’s report for shareholder approval.
- Record Keeping: Maintain proper records of all compliance-related documents, financial statements, auditor’s reports, and meeting minutes to facilitate future audits or inspections.
By following these steps, Section 8 companies can fulfil their annual compliance obligations under the Companies Act, 2013, and maintain good standing with the Registrar of Companies (ROC) while also addressing income tax compliance requirements.
Significance of AOC-4 for Section 8 Companies
The filing of AOC-4 holds significant importance for Section 8 companies, which are not-for-profit entities primarily engaged in charitable and social activities. Here are the key reasons why AOC-4 is significant for Section 8 companies:
- Legal Compliance: AOC-4 filing is a mandatory legal requirement under the Companies Act, 2013. Failure to comply can lead to penalties and legal repercussions. Thus, it ensures that Section 8 companies adhere to statutory regulations.
- Transparency: AOC-4 requires Section 8 companies to disclose their financial information, including the balance sheet, profit and loss account, and cash flow statement. This transparency is essential for maintaining the trust and confidence of donors, members, and other stakeholders.
- Tax Benefits: Compliance with AOC-4 can be crucial for Section 8 companies to avail of tax exemptions and benefits provided by the government. These exemptions can be attractive to potential donors and supporters.
- Stakeholder Trust: Filing AOC-4 instils confidence in the minds of stakeholders, including members, employees, beneficiaries, and the general public. It demonstrates a commitment to transparency and ethical practices.
- Data for Decision-Making: The financial data in AOC-4 can serve as valuable information for the management of Section 8 companies. It can aid in making informed decisions about resource allocation and future projects.
- Legal Protection: Proper AOC-4 filing provides a legal record of the financial health and operations of the Section 8 company. This can offer protection in case of legal disputes or inquiries.
Real-life Examples
- Teach for India: This educational NGO, registered as a Section 8 company, complies with AOC-4 to transparently report its finances. They’ve effectively used these disclosures to attract donors and expand their educational programs.
- Akshaya Patra Foundation: Focused on eradicating hunger among school children, this Section 8 organization diligently files AOC-4 reports. Their compliance has earned the trust of donors and government agencies, ensuring continued support for their mission.
- CRY (Child Rights and You): As a Section 8 company dedicated to child rights, CRY maintains a strong record of AOC-4 compliance. This transparency has bolstered their credibility and enabled them to impact the lives of thousands of children.
- Pratham: A Section 8 organization dedicated to improving education in India, Pratham’s rigorous AOC-4 compliance has helped them secure funding and partnerships for their innovative education programs.
Conclusion
In essence, AOC-4 compliance is indispensable for Section 8 companies in India. These organizations, focused on charitable causes, must adhere to this mandatory financial reporting requirement under the Companies Act, 2013. AOC-4 serves as a pillar of transparency and accountability, showcasing their responsible financial management. By following the prescribed steps, Section 8 companies not only fulfil their legal obligations but also enhance their credibility, attracting vital support from donors and partners who value ethical governance. In essence, AOC-4 is a testament to their commitment to creating a positive societal impact while upholding rigorous standards of corporate governance.


