
In the world of innovation and enterprises, Intellectual property protection becomes the most crucial for creative enterprises. Two important types of Intellectual property rights are Patents and Trademarks. While both protect different valuable assets in their scope and purpose. In this article, we will be going to explore the fundamental differences between trademark and patent. The article, through the light on their unique role and benefits offered by these two intellectual properties to companies and individuals. In case you are an entrepreneur, an inventor, or simply want to know about intellectual property. Then there is a need to understand these two forms of protection.
| Table of Content |
Glimpses of Intellectual property rights
Intellectual property rights are a seat of legal rights that safeguard the creations of the human mind. These creations can take various forms, including inventions, literary and artistic works, designs, symbols, names, and images used in commerce. IPRs aim to incentivize innovation, creativity, and originality by granting exclusive rights to the creators and owners of intellectual property.
Intellectual Property Rights form a critical foundation for incentivizing innovation, creativity, and economic growth while balancing the interests of creators and the public. As technology and globalization continue to advance, the protection and management of IPRs remain vital in shaping our modern knowledge-based society.
What do you mean by Trademark and Patent?
Trademark
A trademark is a distinctive symbol, word, phrase, logo, name, design, product packaging, numerals, slogans, colours and combination of colours thereof that identifies and distinguishes goods or services of one company from those of others. It protects the owner with exclusive rights to use the mark in connection with specific goods or services within a particular geographic region or market segment.
By obtaining trademark registration, a business can prevent others from using a similar or identical mark that could lead to consumer confusion, dilute the brand’s distinctiveness, or potentially harm its reputation. It serves as a unique identifier for a particular brand, allowing consumers to recognize and associate products or services with a specific source or origin.
Patent
A patent is an exclusive right granted by a government to an inventor or assignee for a limited time in exchange for disclosing an invention that is new, non-obvious, and useful. Patents protect inventions, which can be products, processes, machines, compositions of matter, or improvements to existing inventions.
The primary purpose of a patent is to encourage innovation by providing inventors with a temporary monopoly over their inventions. This exclusivity allows inventors to recoup their investment in research and development, gain a competitive advantage in the market, and prevent others from making, using, selling, or importing the patented invention without permission.
Patent e-filing process in India
Difference between Trademark and Patent
Here’s a tabular distinguish between Trademarks and Patents:
| S. No. | Particulars | Trademark | Patent |
|
|
Definition | As per section 2 (1)(zb) of the Trade Marks Act, 1999 “trade mark” means a mark capable of being represented graphically and which is capable of distinguishing the goods or services of one person from those of others and may include the shape of goods, their packaging and combination of colours; | As per section 2 (1)(m) of the Patent Act, 1970 that the “patent” means a patent for any invention granted under this Act; |
| 2. | Purpose | To protect the brand identity and prevent confusion among consumers. | Encourage innovation by granting inventors exclusive rights to their inventions. |
| 3. | Subject Matter | Protects branding elements, such as logos, brand names, patterns, signatures, slogans, etc. | Protects inventions, including products, processes, machines, and compositions of matter. |
| 4. | Duration of Protection | Renewal after 10 years each | Mainly last for 20 years from the filing date of the patent and enters into the public domain |
| 5. | Requirements | Three requirements are:
|
Three requirements are:
|
| 6. | Scope | Particular classes of goods and services | Inventions or designs |
| 7. | Requirement of disclosure | No need for disclosure in public | Needs to disclose the details of inventions in public |
| 8. | For Instances | Xerox, Adidas, MacDonalds, etc. | Formulas related to pharmaceuticals; medical devices, etc. |
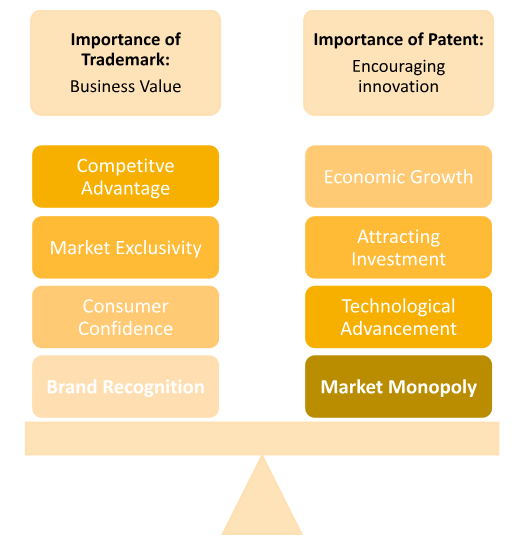
Significance of Trademarks and Patents
Trademarks and patents hold significant importance in the realm of intellectual property protection, fostering innovation, and promoting economic growth. Let’s explore the importance of each:
- Brand Recognition: Trademarks play a crucial role in establishing brand identity. They help consumers easily recognize and differentiate products or services from competitors, building trust and loyalty over time.
- Consumer Confidence: Trademarks provide a sense of consistency and quality assurance to consumers. When a consumer sees a familiar trademark, they know what to expect from the associated products or services, leading to increased confidence in their purchase decisions.
- Market Exclusivity: Trademarks grant businesses exclusive rights to use specific marks for their goods or services in a particular market or industry. This exclusivity protects businesses from unauthorized use by competitors, reducing the likelihood of brand dilution and customer confusion.
- Competitive Advantage: A strong trademark can give a company a competitive edge in the marketplace. It helps create a unique selling proposition, making it easier for businesses to stand out among their peers.
- Business Value: Trademarks can appreciate value over time. As a brand gains recognition and a loyal customer base, the trademark becomes an intangible asset that can add significant value to the business.
Importance of Patents:
- Encouraging Innovation: Patents incentivize inventors and innovators to invest time, effort, and resources into research and development. The promise of exclusive rights encourages them to disclose their inventions to the public, contributing to the pool of knowledge and encouraging further innovation.
- Market Monopoly: Patents provide inventors with a temporary monopoly over their inventions. This exclusivity allows inventors to recoup their investments, reward their creativity, and gain a competitive advantage in the market.
- Technological Advancement: By granting exclusive rights, patents promote the dissemination of knowledge and encourage inventors to build upon existing technologies, leading to further advancements in science and technology.
- Attracting Investment: Patents can make a company more attractive to investors and potential partners. The assurance of protected innovations and potential market dominance can enhance a company’s valuation and growth prospects.
- Economic Growth: A robust patent system fosters economic growth by encouraging innovation, job creation, and increased productivity across various industries.
Takeaway
Through this article, we can say that trademarks and patents are both essential tools for protecting valuable intellectual property, but they address different aspects of innovation and creativity. Whether you are a business owner looking to protect your brand’s reputation or an inventor seeking recognition and reward for your groundbreaking ideas, understanding the differences between trademark and patent is essential. By leveraging these intellectual property protections effectively, individuals and companies can foster growth, establish a competitive edge, and contribute to the collective progress of society.


