
The Goods and Services Tax Return-1 (GSTR-1) form is an essential component of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime, which revolutionized India’s taxation system. It is a return form filed by registered taxpayers to report their outward supplies, providing vital information to tax authorities. GSTR-1 holds significant importance in the GST framework as it serves multiple purposes. Firstly, it allows the government to track and verify the taxable supplies made by businesses, ensuring transparency and preventing tax evasion. Secondly, GSTR-1 aids in the reconciliation of data between businesses, reducing the chances of mismatched information and promoting seamless input tax credit flow. Understanding GSTR-1 is crucial for businesses to ensure compliance with the GST laws. Filing GSTR-1 accurately and on time helps avoid penalties and legal consequences. Additionally, it enables businesses to claim rightful input tax credits, maintain a clean tax record, and establish credibility among suppliers and customers.
|
Table of Content |
Understanding GSTR-1(Meaning)
GSTR-1 is the return form required to be filed by registered taxpayers under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) system. It serves as a comprehensive report of outward supplies made by the taxpayer during a specific tax period. GSTR-1 includes details of all taxable supplies, such as goods or services sold or supplied, along with their corresponding tax amounts. This form captures essential information like invoice-wise details, taxable values, and tax rates applicable to each transaction. By filing GSTR-1 accurately, businesses provide a transparent record of their outward supplies, enabling tax authorities to verify and reconcile the data for efficient tax administration and compliance purposes. The due date for GSTR-1 (Goods and Services Tax Return-1) was the 11th of the following month.
Key Components of GSTR-1
The Key Components of GSTR -1 are: –
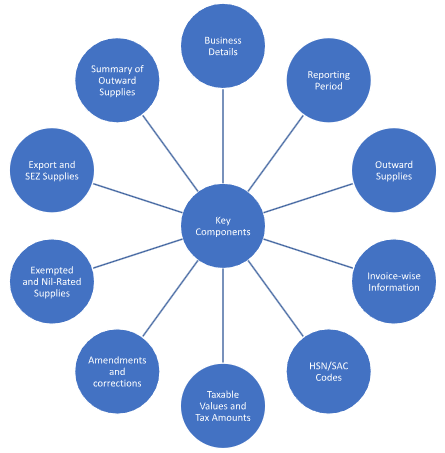
- Business Details: Includes the taxpayer’s legal name, GSTIN, and registration details.
- Reporting Period: Specifies the tax period (monthly or quarterly) for which GSTR-1 is filed.
- Outward Supplies: Details of all taxable supplies made during the reporting period, both inter-state and intra-state.
- Invoice-wise Information: Provides invoice numbers, dates, and values for each taxable supply made.
- HSN/SAC Codes: Specifies the HSN codes for goods or SAC codes for services provided in the supplies.
- Taxable Values and Tax Amounts: Indicates the taxable value of each supply and the corresponding GST rates applied.
- Amendments and Corrections: Allows for amendments or corrections in previously reported invoices or supply details, if required.
- Exempted and Nil-Rated Supplies: Reports supplies that are exempted from GST or subjected to nil GST rates.
- Export and SEZ Supplies: Separately reports supplies made for exports and supplies made to Special Economic Zones (SEZs).
- Summary of Outward Supplies: Provides a summary of all taxable supplies, tax amounts, and the total value of supplies made during the reporting period.
Details Required in GSTR-1
When filing GSTR-1, it is important to provide specific information accurately to ensure compliance with Goods and Services Tax (GST) regulations. The following details need to be reported:
- Invoice-wise Details of Supplies: Each taxable supply made during the reporting period must be reported with invoice numbers, dates, and values. This includes both inter-state and intra-state supplies and is categorized based on the nature of the supply (B2B, B2C, exports).
- Taxable Values: The taxable value of each supply needs to be reported. This represents the value on which GST is applicable, excluding taxes.
- Tax Amounts: The corresponding tax amounts must be reported, indicating the applicable GST rates (CGST, SGST, IGST) for each supply.
- HSN/SAC Codes: The supplies should be associated with the appropriate Harmonized System of Nomenclature (HSN) codes for goods or Services Accounting Codes (SAC) for services.
- Business Details: This includes the legal name, GSTIN (Goods and Services Taxpayer Identification Number), and other registration details of the taxpayer.
- Reporting Period: GSTR-1 is filed for a specific tax period, which can be either monthly or quarterly.
- Amendments and Corrections: Provision to make amendments or corrections to previously reported invoices or supply details, if required.
- Exempted and Nil-Rated Supplies: Reporting supplies that are exempted from GST or subjected to a nil GST rate.
- Export and SEZ Supplies: Separate reporting of supplies made for exports and supplies made to Special Economic Zones (SEZs).
GSTIN of Customers: Accurate reporting of the GSTIN (Goods and Services Taxpayer Identification Number) of customers is crucial. This ensures proper identification of recipients and enables proper reconciliation of data for input tax credit claims.
Amendment and Corrections in GSTR-1
In case there are any errors or omissions in the details provided while filing GSTR-1, the process of amending or correcting them is crucial to ensure accurate reporting. Here is an overview of the process:
- Amendment within the Same Tax Period: If the errors are identified within the same tax period, taxpayers can make amendments in the next filed GSTR-1 to rectify the mistakes. The corrected information should be provided in the relevant sections and fields.
- Amendment in Subsequent Periods: If errors are discovered after the filing of GSTR-1 for a particular tax period, the amendments can be made in the subsequent tax period’s return, i.e., in the GSTR-1 of the subsequent month or quarter.
- Corrections through GSTR-1A: In case amendments are made, the recipient of the supplies will receive an auto-populated document called GSTR-1A, reflecting the changes made by the supplier. The recipient can either accept or reject these amendments.
Role of GSTR-1 in GST Compliance
GSTR-1 plays a crucial role in maintaining transparency within the Goods and Services Tax (GST) system and facilitating compliance. Here’s how GSTR-1 contributes to these aspects:
- Maintaining Transparency: GSTR-1 requires businesses to report all outward supplies made during a specific tax period. By providing detailed information about these supplies, including invoice-wise details, taxable values, and tax amounts, GSTR-1 ensures transparency in the reporting of transactions. This helps tax authorities in verifying the accuracy and authenticity of the reported data, reducing the chances of tax evasion or manipulation.
- Reconciliation of Data: GSTR-1 plays a vital role in reconciling data between different taxpayers. The details reported in GSTR-1 of one taxpayer should match with the corresponding details reported in GSTR-2A (auto-populated return for recipients). Reconciliation helps identify discrepancies, resolve any mismatches, and ensure accurate reporting and reconciliation of supplies between businesses.
- Matching Input Tax Credit (ITC): GSTR-1 data is used for matching the input tax credit claimed by the recipient with the details reported by the supplier in their GSTR-1. This helps in preventing fraudulent or duplicate claims and ensures that the input tax credit is properly matched and utilized. It enhances the accuracy of ITC claims and reduces the possibility of erroneous or fraudulent claims.
Penalties and Consequences of Non-compliance:
Non-compliance with the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regulations, including the filing and submission of GSTR-1, can result in various penalties and consequences. It is important for businesses to understand these repercussions to ensure timely and accurate compliance. Here are some potential penalties and consequences:
- Late Filing Penalty: If a taxpayer fails to file GSTR-1 by the due date, a late filing penalty is applicable. The penalty is typically a fixed amount per day of delay or a percentage of the tax liability.
- Late Payment Interest: In case of delayed payment of the tax liability mentioned in GSTR-1, interest is levied on the outstanding amount. The interest rate is specified by the GST authorities and is calculated from the due date until the payment is made.
- Loss of Input Tax Credit (ITC): Non-filing or incorrect filing of GSTR-1 may result in the loss or denial of input tax credit claimed by the recipient. The recipient’s ability to offset the tax liability against the input tax credit can be affected, leading to additional financial burden.
- Legal Consequences: Continued non-compliance with GST regulations, including GSTR-1 filing, may lead to legal consequences. This can involve legal proceedings, tax audits, investigations, and potential penalties imposed by the tax authorities.
- Reputational Impact: Non-compliance can have a negative impact on the reputation of a business. It may result in a loss of credibility among suppliers, customers, and stakeholders, leading to difficulties in business relationships and potential loss of business opportunities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and complying with GSTR-1 is crucial for businesses operating under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime. GSTR-1 serves as a comprehensive return form that reports outward supplies, ensuring transparency and compliance within the GST system. By providing invoice-wise details of supplies, taxable values, and tax amounts, businesses contribute to maintaining transparency and accurate reporting of transactions. Accurate reporting in GSTR-1 enables smooth data reconciliation, minimizing discrepancies and facilitating the proper utilization of input tax credit. It is essential for businesses to file GSTR-1 accurately and on time, ensuring compliance with GST regulations, and avoiding these potential issues.
In conclusion, businesses should prioritize the accurate filing to fulfill their compliance obligations, contribute to a transparent tax system, and ensure smooth operations within the GST regime.


