
In this article, we will be addressing common questions related to GST return filing, FAQs on GST Returns and concerns on GST returns. Goods and Services Tax (GST) has become an important aspect of taxation in many countries including India. As businesses grapple with the intricacies of GST compliance, it is essential to understand the process of filing GST returns. In this post, we aim to provide concise and informative answers to FAQs on GST Returns. Whether you are a business owner, tax professional, or just an individual seeking clarity on GST returns, this FAQs on GST Returns will serve as a valuable resource to address your queries and guide you through GST returns. Will help navigate the filing process more confidently.
What is GST Return?
A GST return is a document that registered businesses and individuals need to file to report their sales, purchases, and tax liability under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) system. In addition to information like GSTIN, turnover, sales, purchases, input tax credit, tax collected, tax paid, and adjustments, it gives a summary of their financial activity relating to GST.
GST returns are filed to promote tax reconciliation, track tax liability, and maintain openness. They aid tax authorities with confirming tax estimates, ensuring adherence to GST rules, and determining tax liability or GST refund eligibility. Depending on the type of taxpayer and the rules, there are different filing requirements.
What are the different types of GST returns?
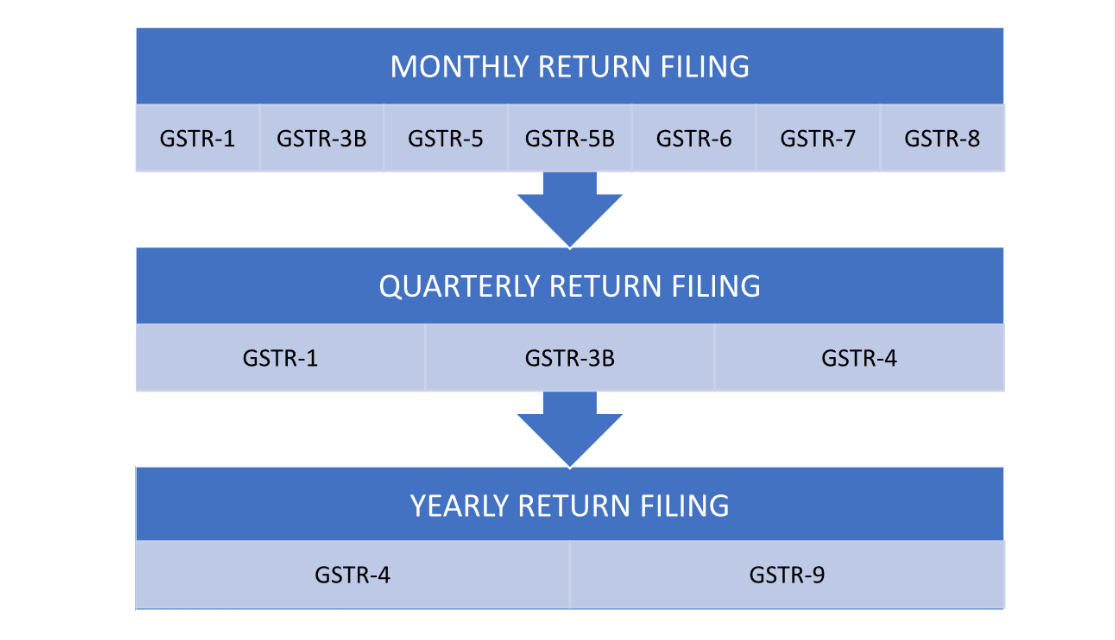
In India, there are several types of GST returns that taxpayers may be required to file. The types of GST returns include:
- GSTR-1: This return is for outward supplies made by registered taxpayers. It includes details of sales made during the reporting period.
- GSTR–2A: Form GSTR-2A is a system generated Statement of Inward Supplies for a recipient.
- GSTR–2B: GSTR 2B is the form issued by the Goods and Services Tax Network, which contains details of inward supplies of goods/services received from registered suppliers.
- GSTR-3B: This is a summary return that provides information on both outward and inward supplies. It also includes the calculation of tax liability and input tax credit.
- GSTR-4: This return is for taxpayers registered under the composition scheme. It includes a summary of quarterly sales, purchases, and tax payable.
- GSTR-5: This return is for non-resident foreign taxpayers who conduct business activities in India. It includes details of sales and purchases made during the reporting period.
- GSTR-6: This return is for Input Service Distributors (ISDs) who distribute input tax credit to other units or branches within the organization. It includes details of input tax credit received and distributed.
- GSTR-7: This return is for taxpayers who are required to deduct tax at source (TDS). It includes details of TDS deducted, along with the TDS certificate.
- GSTR-8: This return is for e-commerce operators who operate online platforms and facilitate the supply of goods or services. It includes details of supplies made through the platform and the tax collected.
- GSTR-9: This is an GST annual return that provides a consolidated summary of all transactions for the entire financial year. It includes details of sales, purchases, input tax credit, and tax liability.
- GSTR-9A: This return is for taxpayers who have opted for the composition scheme. It includes a summary of annual sales, purchases, and tax payable.
- GSTR-9C: This is a reconciliation statement and certification of the annual return for taxpayers whose annual turnover exceeds a specified threshold. It includes the reconciliation of financial statements with the filed GST returns.
Who is required to file GST Return?
The following individuals and entities are required to file GST returns:
- Regular Taxpayers: GST returns must be filed by any organization or individual registered under the GST law in India whose annual revenue exceeds the threshold amount. Businesses, service providers, manufacturers, traders, and experts fall under this category.
- Compositional Plan Taxpayers: Those who choose the GST composition plan are obligated to submit GST returns. Small enterprises with a turnover below the required threshold—currently INR 1.5 crores for most states and INR 75 lakhs for certain north-eastern states—are eligible for the composition scheme.
- Input Service Distributors: ISDs, which are entities that receive invoices for input services and distribute input tax credit to other units or branches of the same organization, are required to file GST returns.
- Non-Resident Taxpayers: GST returns must be filed by non-resident taxpayers who provide taxable products or services in India.
- E-commerce Operators: E-commerce operators that operate online platforms facilitating the supply of goods or services and are involved in collecting and depositing tax on behalf of the suppliers are required to file GST returns.
What information is required to file a GST return?
To file a GST return, you typically need to provide the following information:
- GSTIN (Goods and Services Tax Identification Number): This is a unique identification number assigned to each registered taxpayer.
- Period of the return: You need to specify the reporting period for which the return is being filed (monthly, quarterly, or annually).
- Outward supplies: Details of sales or outward supplies made during the reporting period, including the invoice number, invoice date, customer’s GSTIN (if applicable), taxable value, and applicable tax rate.
- Inward supplies: Details of purchases or inward supplies made during the reporting period, including the invoice number, invoice date, supplier’s GSTIN (if applicable), taxable value, and applicable tax rate.
- Input tax credit: The amount of input tax credit (ITC) availed on purchases made during the reporting period. This includes details of eligible input taxes such as IGST, CGST, and SGST.
- Tax liability: The amount of tax payable on the outward supplies made during the reporting period. This includes the calculation of tax based on the taxable value and applicable tax rate.
- Payments made: Information about tax payments made during the reporting period, including the amount and mode of payment.
- Adjustments or corrections: Any adjustments or corrections made to the previous returns, if applicable.
How do I file GST return?
To file a GST return, you typically need to follow these steps:
- Register for GST: Ensure that you are registered for the Goods and Services Tax (GST) and have obtained a GST identification number (GSTIN).
- Gather Required Information: Collect all the necessary information and documents related to your business transactions, including sales, purchases, input tax credit, and tax payments.
- Access the GST Portal: Log in to the official GST portal of your country. In India, the GST portal is https://www.gst.gov.in/.
- Choose the Correct Return Form: Identify the appropriate return form based on your taxpayer category, reporting period, and the type of return you need to file. For example, GSTR-1 for outward supplies, GSTR-3B for summary returns, etc.
- Fill in the Details: Fill in the required details in the selected return form. Provide accurate information regarding sales, purchases, input tax credit, and tax liability, based on the prescribed format.
- Validate the Return: Validate the return to ensure that all the mandatory fields are filled correctly and there are no errors or omissions.
- Pay Tax: Calculate the tax liability based on the information provided in the return and pay the tax amount, if applicable, using the available payment options on the GST portal.
- Submit the Return: Once all the information is filled in accurately, review the return form and submit it electronically on the GST portal and pay the necessary GST return filing charges. After submission, you will receive an acknowledgment or a reference number.
- File Nil Return: If you have not made any sales or purchases during the reporting period, you may still need to file a GST nil return to indicate zero transactions.
- Reconcile and Maintain Records: Keep a copy of the filed return, along with all supporting documents, for your records. Ensure that your books and records reconcile with the information provided in the GST return.
Due date of filing GST return
The due of filing GST return are:
- GSTR-1 (Monthly return for outward supplies): 11th of the next month
- GSTR-3B (Monthly return for summary of outward and inward supplies): 20th of the next month
- GSTR-4 (Quarterly return for composition dealers): 18th of the month succeeding the quarter
- GSTR-5 (Return for non-resident foreign taxpayers): 20th of the next month
- GSTR-6 (Return for input service distributors): 13th of the next month
- GSTR-7 (Return for tax deducted at source): 10th of the next month
- GSTR-8 (Return for e-commerce operators): 10th of the next month
- GSTR-9 (Annual return): 31st December of the year following the relevant financial year.
Can I revise my GST return if I make an error?
Yes, it is possible to revise a GST return if you have made an error or omission in the original filing. The Goods and Services Tax (GST) system allows taxpayers to rectify mistakes by filing a revised return. However, there are certain conditions and limitations to keep in mind:
- Time limit: The revision of a GST return can only be done within a specified time limit.
- Corrections allowed: To address inaccuracies or omissions in the initial return, revised returns may be filed. Correcting errors in the reporting of sales, purchases, input tax credits, tax liabilities, or any other pertinent information falls under this category.
- Conditions for revision: Generally, a return may only be revised if the original return was submitted by the deadline. The first return might not be eligible for amendment if it was submitted after the deadline.
- Amendment of details: Details that need to be changed can be changed or amended while updating a tax return. In the revised return, it’s crucial to include correct and current information.
What happens if I don’t file my GST return?
Failing to file your GST return can have several consequences, which may vary depending on the jurisdiction and the specific regulations in place. Here are some common repercussions of not filing GST returns:
- Penalties and Late Fees: Most tax authorities impose penalties and late fees for non-compliance with GST return filing requirements. These penalties can be a fixed amount or calculated based on a percentage of the tax liability.
- Loss of Input Tax Credit: In some situations, you may lose the ability to claim input tax credits (ITCs) on your purchases if you don’t submit your GST returns by the deadline. As a result, you won’t be able to use the tax you paid on purchases to offset the tax you owe on sales.
- Legal Repercussions: Failure to comply with the requirements for completing a GST return may result in tax audits, investigations, or even legal action. To guarantee that tax laws are being followed, tax authorities have the authority to adopt enforcement measures.
- Business Disruption: Failing to submit GST returns might have a detrimental effect on how your company conducts business. It can make it more difficult for you to apply for financial aid or loans, participate in government contracts, or get licenses or permits.
- Discrepancies and reconciliation: Failure to file GST returns may result in errors and inconsistencies in your tax records. This may generate questions during tax audits or assessments and make it difficult to reconcile your tax liability and collect input tax credits.
To prevent these repercussions, it’s critical to adhere to the filing requirements for GST returns and follow the established timeframes.
Takeaway
In this article, we have gone through the frequently asked questions on GST returns in detail. In order to maintain compliance with the tax law, it is important for both businesses and individuals to understand the nuances of filing GST returns. We have addressed various frequently asked questions regarding GST return filing in this FAQ article. Taxpayers can speed up their GST return filing by understanding these considerations and reduce the chances of mistakes or non-compliance. After reading this FAQ article taxpayers can explore the world of GST return filing with confidence and efficiency.


